Ansible 安装与配置
Vultr 私有网络配置
-
Deploy new Server 时选中 “Private Network”。推荐 Los Angeles 节点的服务器。D瓜哥感觉没啥用,但是选上吧。
-
打开 Private Networks,点击 Add Network 按钮,
-
Location— 选中和上述服务器节点相同的地点 -
Description— 起个名字,方便识别 -
Network— 这个可以设置私有网络的网段,根据自己的需要设置,比如D瓜哥设置的是172.16.0.0/16。
-
-
打开刚刚新建的服务器的设置页面,如下:
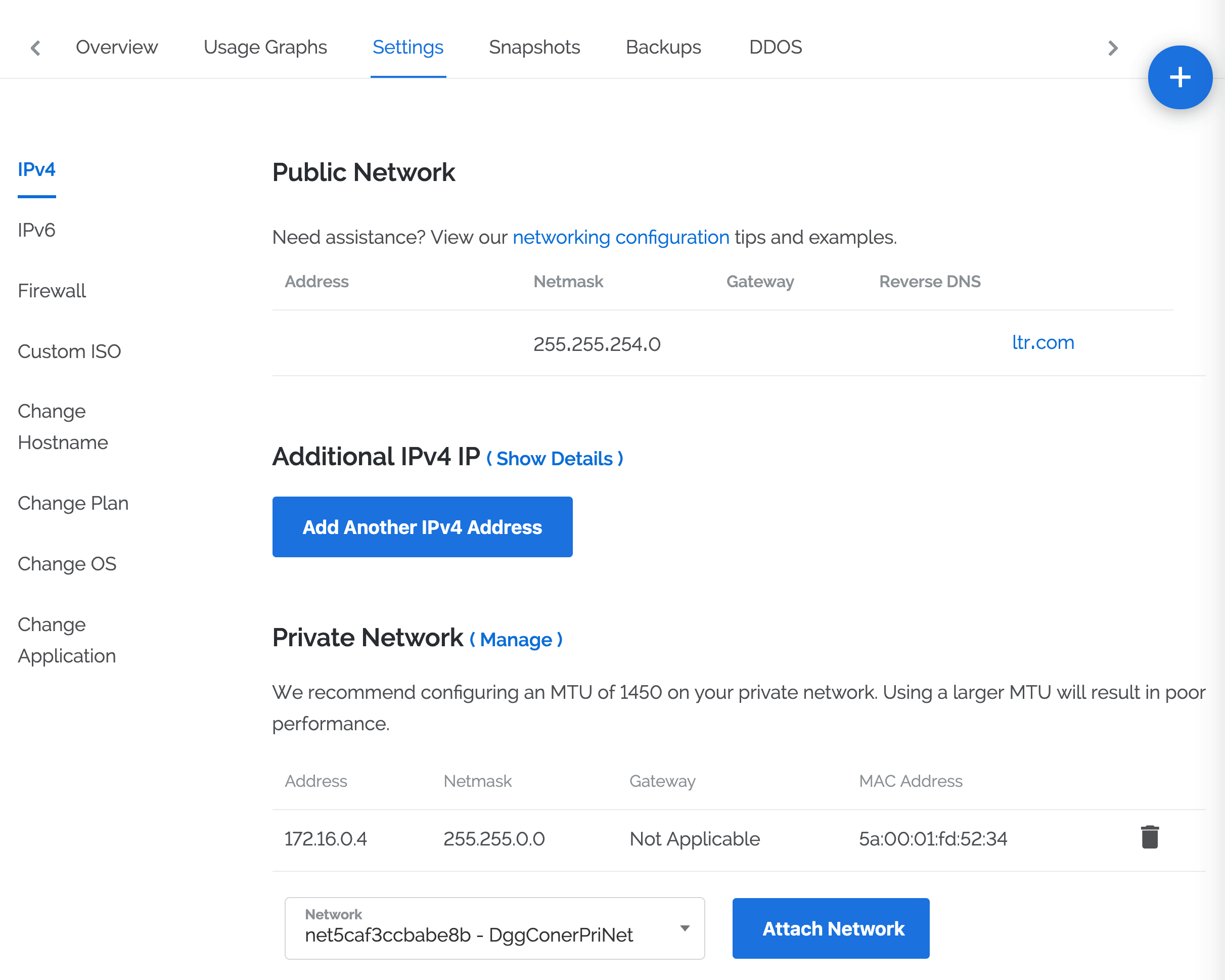 Figure 1. vultr private network
Figure 1. vultr private network-
在最下面
Network中选择刚刚新建的网络中Description设置的名字的子网,然后点击Attach Network创建私有网络IP。 -
然后,注意刚刚点击按钮上面的网络 IP 地址以及 MAC Address 地址。
-
-
Configuring Private Network 中有各个系统的私有网络设置。D瓜哥 用的是 Ubuntu 18.04,下面细说一下 Ubuntu 18.04 的配置。
-
ssh到刚刚创建的服务器上面,然后打开/etc/netplan/10-ens3.yaml,然后再下面添加ens7的以太网配置。# vim /etc/netplan/10-ens3.yaml network: version: 2 renderer: networkd ethernets: ens3: dhcp4: yes ens7: match: macaddress: 5a:00:01:fd:53:06 (1) mtu: 1450 dhcp4: no addresses: [172.16.0.3/16] (1)1 这里的 IP 和 Mac Address 就是上面的提到的 IP 和 Mac Address 。 -
配置完成后,重启网络
netplan apply,然后ifconfig就可以看到ens7的网络信息了。 -
多台服务器之间,按照这个模式配置起来,需要同一个子网下的,就选择同一个子网。可以相互
ping一下测试网络连通情况。
Ansible 的安装与设置
$ sudo apt-get update
$ sudo apt-get install software-properties-common
$ sudo apt-add-repository --yes --update ppa:ansible/ansible
$ sudo apt-get install ansible控制主机:用于控制其它机器的主机 管理主机:被控制主机管理的主机
一台控制主机:
node1: 172.16.0.3
两台管理主机:
node2: 172.16.0.4 node3: 172.16.0.5
-
配置管理主机:在控制主机上,执行
vim /etc/ansible/hosts,然后在最下面输入如下内容:172.16.0.4 172.16.0.5 -
在控制主机上,生成 SSH 密钥对
ssh-keygen -C node1 -
将公钥拷贝到每台管理主机的
.ssh/authorized_keysssh-copy-id -i ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub root@172.16.0.4 ssh-copy-id -i ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub root@172.16.0.5 -
Ansible 配置
vim /etc/ansible/ansible.cfg-
禁用每次执行ansbile命令检查ssh key host
host_key_checking = False -
开启日志记录
log_path = /var/log/ansible.log -
ansible连接加速配置
[accelerate] accelerate_port = 5099 #accelerate_port = 10000 #accelerate_timeout = 30 #accelerate_connect_timeout = 5.0 # If set to yes, accelerate_multi_key will allow multiple # private keys to be uploaded to it, though each user must # have access to the system via SSH to add a new key. The default # is "no". accelerate_multi_key = yes
-
-
测试
ansible all -m ping$ ansible all -m ping 172.16.0.5 | SUCCESS => { "changed": false, "ping": "pong" } 172.16.0.4 | SUCCESS => { "changed": false, "ping": "pong" } # as bruce $ ansible all -m ping -u bruce # as bruce, sudoing to root $ ansible all -m ping -u bruce --sudo # as bruce, sudoing to batman $ ansible all -m ping -u bruce --sudo --sudo-user batman # With latest version of ansible `sudo` is deprecated so use become # as bruce, sudoing to root $ ansible all -m ping -u bruce -b # as bruce, sudoing to batman $ ansible all -m ping -u bruce -b --become-user batman $ ansible all -a "/bin/echo hello"
Ansible 使用
/etc/ansible/ansible.cfg – Config file
~/.ansible.cfg – User config file, overrides the default config
ansible
is an extra-simple tool/framework/API for doing ‘remote things’. this command allows you to define and run a single task ‘playbook’ against a set of hosts
ansible-console
a REPL that allows for running ad-hoc tasks against a chosen inventory (based on dominis’ ansible-shell).
ansible-doc
displays information on modules installed in Ansible libraries. It displays a terse listing of plugins and their short descriptions, provides a printout of their DOCUMENTATION strings, and it can create a short “snippet” which can be pasted into a playbook.
ansible-galaxy
command to manage Ansible roles in shared repositories, the default of which is Ansible Galaxy https://galaxy.ansible.com.
ansible-playbook
the tool to run Ansible playbooks, which are a configuration and multinode deployment system. See the project home page (https://docs.ansible.com) for more information.
ansible-pull
pulls playbooks from a VCS repo and executes them for the local host
is used to up a remote copy of ansible on each managed node, each set to run via cron and update playbook source via a source repository. This inverts the default push architecture of ansible into a pull architecture, which has near-limitless scaling potential.
The setup playbook can be tuned to change the cron frequency, logging locations, and parameters to ansible-pull. This is useful both for extreme scale-out as well as periodic remediation. Usage of the ‘fetch’ module to retrieve logs from ansible-pull runs would be an excellent way to gather and analyze remote logs from ansible-pull.

